- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Tinea Versicolor and Irritant Dermatitis
For 10 years, a 32-year-old woman has had an asymptomatic rash on both sides of her neck. She is otherwise healthy.Do you recognize this rash?
Case 1:
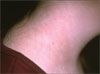
For 10 years, a 32-year-old woman has had an asymptomatic rash on both sides of her neck. She is otherwise healthy.
Do you recognize this rash?
A. Acanthosis nigricans.
B. Tinea versicolor.
C. Tinea corporis.
D. Atopic dermatitis.
E. Poikiloderma of Civatte.
(answer on next page)
Case 1: Tinea versicolor
A potassium hydroxide evaluation confirmed the diagnosis of tinea versicolor, B, which responded to a short course of oral ketoconazole. Acanthosis nigricans has a more velvety appearance. Tinea corporis would be more inflammatory and pruritic, as would atopic dermatitis. Poikiloderma of Civatte is characterized by mottled pigmentation and telangiectasia without scale.
Case 2:

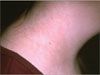
A 44-year-old man has a dry, itchy rash on his neck that seems to be aggravated by shaving. He has not changed his shaving cream and does not use aftershave.
What do you suspect?
A. Dermatophyte infection.
B. Impetigo.
C. Candidiasis.
D. Nummular eczema.
E. Irritant dermatitis from shaving.
(answer on next page)
Case 2: Irritant dermatitis
This patient had recently started to use a new 5-bladed razor; his “close shave” resulted in irritant dermatitis, E. Switching to a razor with fewer blades and applying a moisturizer as an aftershave resolved the problem.
Nummular eczema and dermatophyte and candidal infections usually do not occur on the neck. Impetigo has a more crusted appearance.
Case 3:
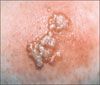
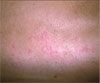
For 3 days, a 28-year-old woman has had a tender eruption on her posterior right thigh. She has no history of a similar eruption. She is otherwise healthy but had seasonal allergies as a child. Recently, she has started using new brands of soap and shaving cream. Can you identify this eruption?
A. Staphylococcal infection.
B. Fixed drug eruption.
C. Herpes simplex virus infection.
D. Contact dermatitis.
E. Nummular eczema.
(answer on next page)
Case 3: Herpes simplex virus infection
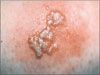
A culture identified herpes simplex virus type 2, C. Treatment with oral antiviral antibiotics was started. The patient was counseled about being evaluated for other sexually transmitted diseases and the ramifications of genital herpes infections.
Bullous impetigo from a staphylococcal infection usually produces more fragile blisters. A fixed drug eruption is a possibility if a relevant history can be obtained; otherwise, a biopsy would confirm the diagnosis. Contact dermatitis is unlikely because of the lack of exposure history and the absence of pruritus. Nummular eczema is pruritic and does not form blisters.
Case 4:
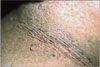
A 20-year-old African American man seeks evaluation of discoloration of his neck. The rash has been present for at least several months. The patient is obese but otherwise healthy.
What is your clinical impression?
A. Erythrasma.
B. Candidiasis.
C. Intertrigo.
D. Acanthosis nigricans.
E. Contact dermatitis.
Bonus question: What malignancy is most commonly associated with this condition?
(answer on next page)
Case 4: Acanthosis nigricans
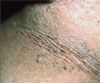
A hyperpigmented rash on the neck of an overweight man is likely to be acanthosis nigricans, D. Insulin resistance is often present in obese persons with this rash. There is no specific treatment; however, weight reduction and correction of hyperinsulinemia may help resolve the rash.
In addition to obesity-associated acanthosis nigricans, the following types have been recognized:
•Syndromic. The type A syndrome is also termed the hyperandrogenemia, insulin resistance, and acanthosis nigricans syndrome (HAIR-AN syndrome). The type B syndrome generally occurs in women who have uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, ovarian hyperandrogenism, or an autoimmune disease.
•Acral. This type is most common in persons who have dark skin.
•Unilateral. This condition probably represents a type of mosaicism that is not well understood.
•Familial. This rare genodermatosis seems to be transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion.
•Malignant.
•Drug-induced.
•Mixed type.
This patient also had a number of acrochordons, or skin tags, which occur most often in persons who are overweight or who have diabetes. The other conditions in the differential-erythrasma, candidiasis, intertrigo, and contact dermatitis- are all symptomatic and feature scaling or maceration.
Answer to bonus question: The malignancy most commonly associated with acanthosis nigricans is adenocarcinoma of the GI tract.
