- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
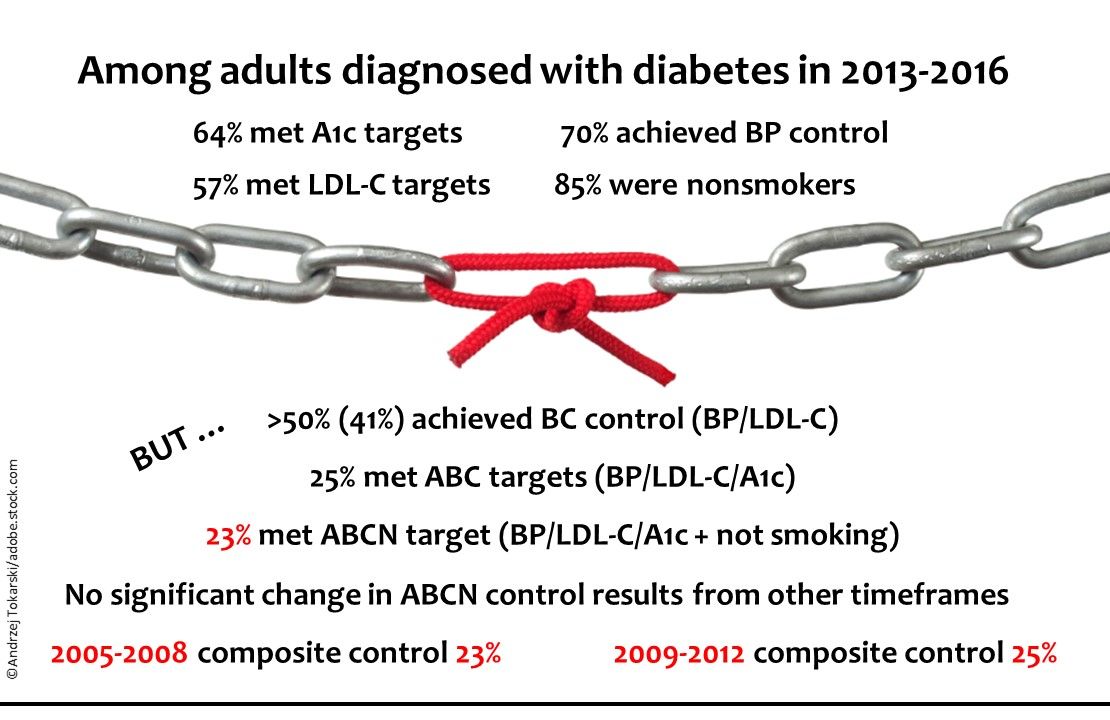
Health of US Diabetes Patients Largely Unchanged since 2005
US adults with type 2 diabetes have acheived negligible change in blood glucose levels, blood pressure, LDL-C levels, and smoking status in the past 15 years, according to a new study.
Outcomes for US adults with diabetes along 3 essential measures of metabolic health remained essentially unchanged between 2005 and 2016, according to a new study.
Investigators from the Massachusetts General Hospital found that fewer than 1 in 4 American adults diagnosed with diabetes met disease control targets for blood sugar, blood pressure, or cholesterol. Rates of smoking cessation, also a goal of diabetes treatment, have stagnated as well. The study was published JAMA Internal Medicine online on August 12, 2019.
In a hospital news release lead author Pooyan Kazemian, PhD, said "Our results suggest that, despite major advances in diabetes drug discovery and movement to develop innovative care delivery models over the past two decades, achievement of diabetes care targets has not improved in the United States since 2005." (See Figure below)
Diabetes affects 30.2 million US adults with prevalence expected to reach 54 million by 2030.
Diabetes affects 30.2 million US adults with prevalence expected to reach 54 million by 2030. It is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease and mortality as well as of significant disability related to micro- and macrovascular complications.
Serial NHANES data
Study authors analyzed serial cross-sectional studies included in the 2005-2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (n = 1742 diagnosed and 746 undiagnosed) to evaluate the cascade of diabetes care (ie, diabetes diagnosis, linkage to care, and achievement of treatment targets) in the United States.
They were also interested in potential disparities in diabetes care related to age, gender, and race.
Primary outcome measures were proportion of participants overall and stratified by age, sex, and race/ethnicity who were linked to diabetes care and met glycemic (A1c <7.0%-8.5%, depending on age, complications), blood pressure (<140/90 mm Hg), cholesterol level (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL), and smoking abstinence targets and a composite of all targets.
Odds of achieving the composite target comprised of blood sugar, blood pressure, cholesterol, and non-smoking were lower among younger participants (aged 18-44 years), among women, and among non-white adults with diabetes.
Insurance coverage was the strongest indicator of diagnosis, linkage, and achievement of the composite treatment targets.
The LDL-C target was the least likely of the 3 to be met, even though elevated lipids may be relatively easier to treat than hypertension and hyperglycemia, the authors point out.
Only 6 in 10 adults with diagnosed diabetes were prescribed a statin in the 2013-2016 study period, even though there was modest growth in the use of statins over the 3-study time frame.
Next: Implications for US diabetes care
Implications for US diabetes care: Interventions to help promote early control of risk factors in younger patients, the authors suggest, would help slow or curtail the progression of complications that lead to diabetes morbidity and mortality. Sex disparities in cardiovascular care, they point out, as well as access to care, may have contributed overall to sex disparities in diabetes care.
In their discussion of the results the authors state: “ …while there may be some underlying physiologic differences in the prevalence of hypertension and insulin deficiency that correlate with race/ethnicity…access to and effectiveness of health care remain major factors that have not been adequately addressed on a population level despite numerous innovative interventions targeting these populations.”
Devising population-level strategies to improve care of diabetes in the United States will require consistent monitoring of the diabetes care cascade, the authors note. They conclude with the admonition that the significant advances in treatment of diabetes are only successful when they reach the populations at greatest risk.
_______________________________________________________
Stay in touch with Patient Care® Online
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Like us on Facebook
Follow us on Twitter
Write or Blog for Patient Care® Online
