- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Dermatophytosis (Tinea) That Resembles Necrobiosis Lipoidica
Always check the toenails for fungal infection after diagnosing tinea pedis, corporis, or cruris. The toenails may act as the source of infection and a reservoir, which may lead to reinfection after the cutaneous dermatophytosis is cleared.
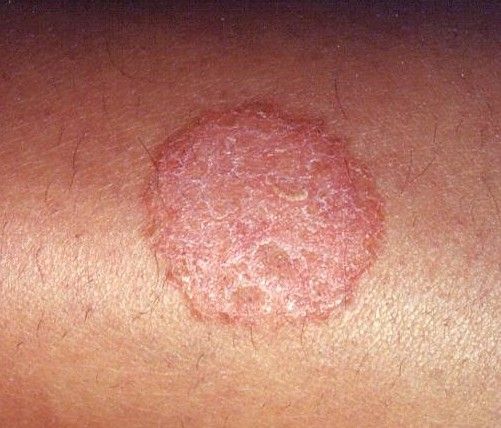
A 52-year-old man was annoyed by a solitary itchy patch on his anterior foreleg. He was in good health except for type 2 diabetes mellitus and mild hypertension.
Key point: The plaque looks similar to and should suggest necrobiosis lipoidica because of its shape and location. However, unlike the latter, this lesion is surmounted by significant scale formation. A KOH preparation was positive, which verified the presumptive diagnosis of dermatophytosis (tinea).
Treatment: Application of 2% naftifine cream once daily for 2 weeks led to resolution of the fungal infection. The patient refused treatment for his obvious onychomycosis.
Note: Always check the toenails for fungal infection after diagnosing tinea pedis, corporis, or cruris. The toenails may act as the source of infection and a reservoir, which may lead to reinfection after the cutaneous dermatophytosis is cleared.
