- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Dermatophytosis
This solitary, very pruritic, annular lesion suggests dermatophytosis. KOH preparation verified the presence of Tinea faciei. This infection is usually associated with contact with a new kitten or puppy.
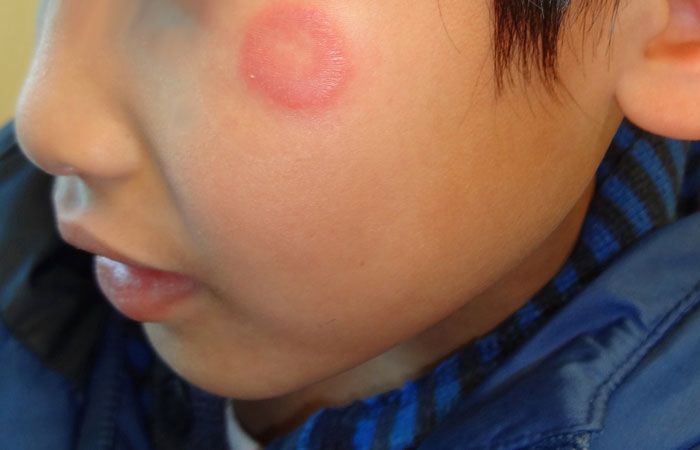
A 7-year-old boy presented with a solitary, nearly circular, very pruritic inflammatory facial lesion. He was otherwise in good health.
Key point: Annular lesions suggest dermatophytosis. The intensity of the inflammatory response suggests a non-human source for the fungus (the presence of which was verified by potassium hydroxide preparation).
Treatment: Twice-daily application of sertaconazole 2% cream led to prompt resolution of this prototypical case of tinea faciei.
Note: Most of the time, this phenomenon is associated with acquisition a new kitten or puppy. In this case, the child had contact with a new kitten while playing at a friend’s house.
