- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Surgical Treatment of Obesity: Questions Physicians Often Ask About Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding
Because bariatric surgery has traditionally been associated with a high incidence of complications, it has been used primarily for superobese patients. A large body of evidence suggests that laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is a much safer procedure that is also very effective. This procedure offers an additional option to patients who might benefit from bariatric surgery when diet, exercise, and pharmacologic approaches have failed. Here we address questions primary care physicians often ask about the procedure.
Given the rapid rise in the prevalence of obesity-which now stands at 27% of the adult US population1-there is an urgent need for the development of safe and effective treatments. Obesity causes approximately 300,000 deaths annually and is associated with significant morbidity.1,2 Hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease, sleep apnea, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux, degenerative joint disease, parenchymal liver disease, infertility, and a number of malignancies occur more frequently or are more severe in obese persons.
Surgical procedures are indicated for persons with very severe obesity. These procedures can result in significant weight loss that is maintained for 5 years or more. Weight loss is accompanied by amelioration of comorbid conditions and increased activity levels.
Because bariatric surgery has traditionally been associated with a high incidence of complications, it has been used primarily for superobese patients. A large body of evidence suggests that laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is a much safer procedure that is also very effective. This procedure offers an additional option to patients who might benefit from bariatric surgery when diet, exercise, and pharmacologic approaches have failed. Here we address questions primary care physicians often ask about the procedure.
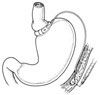

1. What is laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, and how does it differ from other bariatric surgical procedures?
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is a restrictive bariatric procedure that was developed in the 1990s and approved by the FDA in 2001. It involves laparoscopic placement of a silicone band around the upper stomach (Figure).3 The band is connected through a catheter to a subcutaneous reservoir into which saline solution can be injected to adjust the diameter of the band.4 Following this procedure, patients experience early satiety and slow emptying of gastric contents because of the restriction caused by the band.4
Other restrictive procedures include vertical gastric banding (Table), which will likely be supplanted by laparoscopic gastric banding, a safer procedure. Malabsorptive procedures include biliopancreatic diversion with or without duodenal switch and distal gastric bypass. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a combined restrictive and malabsorptive procedure that is currently the most popular bariatric procedure in the United States.
2. What are the benefits of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding?
This procedure offers the advantages of minimal (overnight) hospital stay, less pain, and early return to normal activities, as well as adjustability and complete reversibility. Technically, it is easier to perform than other bariatric procedures. Unlike malabsorptive procedures, it is not followed by mineral and vitamin deficiencies and dumping syndrome. The adjustability feature allows progressive and gradual weight loss. It also allows for limiting the gastric restriction if the patient becomes pregnant, has a gastric disorder, or requires a medication that has gastric toxicity.
The weight loss following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is associated with resolution or remission of diabetes in about two thirds of patients and improved glycemic control in the remainder.5 Hypertension and sleep apnea resolve in many cases.6,7 Asthma improves significantly,8 and gastroesophageal reflux is corrected.9 Many obese infertile women become ovulatory within the first postoperative year.10
These health benefits are associated with other bariatric procedures as well, but often at the expense of more severe side effects (including more dietary restrictions and the risk of vomiting and malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies).
3. Which patients are candidates for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding?
Good candidates are:
- Patients between the ages of 18 and 65 years with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 35 who have comorbid conditions.
- Patients with a BMI greater than 40 with or without comorbidities,11 who have a history of successful attempts to lose weight (at least 10 lb).12
These patients should be committed to postoperative dietary compliance, because the intake of high-calorie liquids and soft foods, such as milkshakes and ice cream, will hinder weight loss. Some experts consider sweet-eating behavior a contraindication to this procedure13; others do not.14
Patients should have realistic expectations about the risks and benefits of this procedure. Most important, this operation should not be performed for cosmetic reasons alone.
Persons who are poor candidates for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding include those with cardiovascular disease, acute GI disease, and active psychiatric illness (including eating disorders). It is also not indicated for those with cirrhosis, portal hypertension, or a history of gastric ulcer or those receiving long-term corticosteroid therapy. Persons with connective tissue disease may be considered for the procedure because an adjustment can be made when systemic corticosteroids or high-dose anti-inflammatory agents are needed.
4. What is included in the preoperative evaluation?
Patients undergo a comprehensive medical evaluation, including cardiac clearance for surgery, upper endoscopy, and evaluations by a nutritionist and a psychiatrist. Those with active medical or psychiatric disorders should not undergo the procedure. Patients must understand that they play a crucial role in achieving a successful outcome and should agree to comply with a diet and exercise program.
5. How much weight loss can be expected following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding compared with weight loss following other bariatric procedures?
Most studies show that patients lose an average of 40% to 50% of their excess body weight after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding.15,16 US studies show a range of 31% to 61% weight loss at 1 year, 43% to 75% at 2 years, 56% to 72% at 3 years, and 60% at 4 years.17,18 Some studies from other countries suggest even greater efficacy. Weight is lost slowly and progressively over a 4-year period. The amount of weight lost is comparable to that seen with other restrictive bariatric procedures, such as vertical gastric banding.15
In contrast, weight loss following malabsorptive surgical procedures (biliopancreatic diversion and distal gastric bypass) occurs more abruptly. Patients lose about 75% to 80% of excess body weight over 3 to 5 years.16 The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is associated with a 60% to 70% excess body weight loss after 3 to 5 years.16
6. What is the usual follow-up regimen after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding?
Postoperative management includes a liquid diet for the first 2 to 4 weeks, after which soft and then solid foods are introduced.19 Food should be eaten slowly and chewed thoroughly. Liquids should have no calorie content and should be consumed 10 minutes before or 90 minutes after the meal.19 Patients are expected to lose weight at the rate of 0.5 to 1 kg per week.
The first adjustment of the gastric band is done 5 to 7 weeks after the procedure.4 A typical patient undergoes 3 to 6 adjustments during the first postoperative year.19
It is important thatpostoperative follow-up visits be scheduled 6 weeks after the procedure and then monthly for the first year.20 Because ofthe expected changes in hypertension, diabetes, and other chronic conditions often associated with obesity, patients frequently require decreased dosages or discontinuation of medications.
During follow-up visits, patients' weight loss is evaluated and BMI is calculated. They are evaluated for possible complications from the procedure, and comorbidities are monitored. Band adjustments are performed by the surgeon when weight loss reaches a plateau. Consultation with a dietitian is essential, both preoperatively and after the procedure.
A major advantage of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding is that patients do not have the significant dietary limitations associated with other bariatric procedures. They may eat a regular diet-although in very small portions. A low-calorie, low-fat diet increases postoperative weight loss. High-calorie liquids and soft foods-such as sodas, milkshakes, juices, and ice cream-should be avoided. Advise patients to exercise. Any cardiovascular program that is recommended for patients who are trying to lose weight is appropriate.
7. What are the most common complications after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, compared with other bariatric procedures?
Possible complications of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding include gastric pouch dilatation, port-tube complications, band erosion, gastric prolapse, and reservoir leakage. Although direct comparison trials are lacking, the overall morbidity rate is 11.3%, compared with 23.6% for vertical banding gastroplasty and 25.7% for Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.5No associated mortality has been reported with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding.21
Diarrhea and constipation are not associated with laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Vomiting may occur; the incidence varies from 0% to 60%.21
References:
REFERENCES:
1. National Center for Health Statistics. Data and Statistics: Overweight and obesity trends among adults. Atlanta: National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and prevention. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/index.html. Accessed June 3, 2004.
2. Field AE, Coakley EH, Must A, et al. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1581-1586.
3. Belachew M, Zimmerman JM. Evolution of a paradigm for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Am J Surg. 2002;6(suppl 2):21S-25S.
4. Fielding GA, Allen JW. A step-by-step guide to placement of the LAP-BAND adjustable gastric banding system. Am J Surg. 2002;6(suppl 2):26S-30S.
5. Dixon JB, O'Brien P. Health outcomes of severe-ly obese type 2 diabetic subjects 1 year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:358-363.
6. Bacci V, Basso MS, Greco F, et al. Modification of metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors after weight loss induced by laparoscopic gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2002;12:77-82.
7. Dixon JB, Schachter LM, O'Brien PE. Sleep disturbance and obesity: changes following surgically induced weight loss. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:102-106.
8. Dixon JB, Chapman L, O'Brien P. Marked improvement in asthma after LAP-Band surgery for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 1999;9:396-398.
9. Angrisani L, Iovino P, Lorenzo M, et al. Treatment of morbid obesity and gastroesophageal reflux with hiatal hernia by LAP-BAND. Obes Surg. 1999;9: 396-398.
10. Martin LF, Finigan KM, Nolan TE. Pregnancy after adjustable gastric banding. Obstet Gynecol. 2000;95:927-930.
11. National Institutes of Health. The Practical Guide: Identification, Evaluation and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and North American Association for the Study of Obesity; 2000. NIH publication 00-4084:1-94.
12. Dixon JB, O'Brien PE. Selecting the optimal patient for LAP-BAND placement. Am J Surg. 2002;6 (suppl 2):17S-20S.
13. Lindroos AK, Lissner L, Sjostrom L. Weight change in relation to intake of sugar and sweet foods before and after weight reducing gastric surgery. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996;20:634-643.
14. Busetto L, Segato G, De Marchi F, et al. Outcome predictors in morbidly obese recipients of an adjustable gastric band. Obes Surg. 2002;12:83-92.
15. O'Brien P, Dixon JB. Weight loss and early and late complications: the international experience. Am J Surg. 2002;6(suppl 2):42S-45S.
16. Fisher BL, Schauer P. Medical and surgical options in the treatment of severe obesity. Am J Surg. 2002;6(suppl 2):4S-8S.
17. Spivak H, Anwar F, Burton C, et al. The Lap-Band system in the United States. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:198-202.
18. Ren CJ, Weiner M, Allen JW. Favorable early results of gastric banding for morbid obesity. The American experience. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:543-546.
19. Favretti F, O'Brien P, Dixon JB. Patient management after LAP-BAND placement. Am J Surg. 2002;6 (suppl 2):38S-41S.
20. Shen R, Dugay G, Rajaram K, et al. Impact of patient follow-up on weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2004;14:514-519.
21. Chapman AE, Kiroff G, Game P, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of obesity: a systematic review. Surgery. 2004;135: 326-351.
