- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Rosacea and Polymorphous Light Eruption in a Young Woman
Is this acneform eruption on a middle-aged woman’s face perioraldermatitis? Rosacea? Pyoderma faciale? Is this pruritic rash related to ayoung woman’s tanning salon visits? Scrutinize the photos, make yourdecisions, and compare your answers with an expert’s.
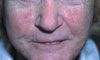
Case 1:
A 57-year-old woman presents with an asymptomatic acneform eruption on the midface that is accompanied by episodes of erythema that last for hours to days. She is otherwise healthy and takes no medication.
What is the likely cause of the eruption?
A.
Perioral dermatitis.
B.
Contact dermatitis.
C.
Rosacea.
D.
Pyoderma faciale.
E.
Pityrosporum
folliculitis.
Which of the following topical treatment options are appropriate?
F.
Erythromycin.
G.
Clindamycin.
H.
Azelaic acid.
I.
Sulfur.
J.
Triamcinolone 0.1%
K.
Hydrocortisone 1%
L.
Hydrocortisone 2.5%
M.
Metronidazole
Which of the following oral treatment options are appropriate?
N.
Tetracycline.
O.
Doxycycline.
P.
Prednisone (6-day taper).
Q.
Erythromycin.
R.
Metronidazole.
S.
Isotretinoin
T.
Amoxicillin
(Answer on next page.)

Case 1:
The patient has
rosacea, C.
This chronic condition is characterized by erythema and edema, papules, pustules, and telangiectasia.Recent evidence suggests that
Bacillus
species play a role in rosacea, which supports the traditionaltreatment options of topical and oral antibiotics. All the choices listed are appropriate treatment options, except for
J, K,
and
P.
Further study is needed to elucidate the other factors involved in the development of rosacea.
Perioral dermatitis is confined to the region around the mouth. Contact dermatitis is pruritic and does not produce pustules. Pyoderma faciale is inflammatory and features cysts and nodules. Pityrosporum folliculitis is pruritic.
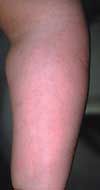
Case 2:
Pruritic red patches have developed on the trunk and extremities of a 25-year-old woman following her first session at a tanning salon after a hiatus of several months. She had previously visited the salon on several occasions, with no ill effects. Treatment with an over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream has been ineffective. The patient takes no medication other than an oral contraceptive.
What are you looking at here?
A.
Polymorphous light eruption
B.
Urticaria
C.
Erythema multiforme
D.
Tinea versicolor
E.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
(Answer on next page.)

Case 2:
The patient has
polymorphous light eruption, A,
which developed as an allergic reaction to the UV light in the tanning salon. Treatment consists of avoidance of sun exposure and tanning salons. Some patients respond to treatment with dapsone or hydroxychloroquine.
Urticaria consists of erythematous wheals that appear and resolve within 24 hours. Erythema multiforme manifests as tender, nonpruritic patches. Tinea versicolor features scaling hypopigmented or hyperpigmented patches that appear primarily on the trunk. The lesions of systemic lupus erythematosus, which mimic polymorphous light eruption, are large, tender patches on sun-exposed surfaces. The definitive diagnosis is made by biopsy.
