- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Proliferating Actinic Keratosis
The redness on this woman's nose represents fairly severe photodamage with extensive actinic keratosis. Use of a topical therapy to achieve clearance of a field of actinic damage can be done with imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil, or ingenol mebutate creams, or diclofenac gel.
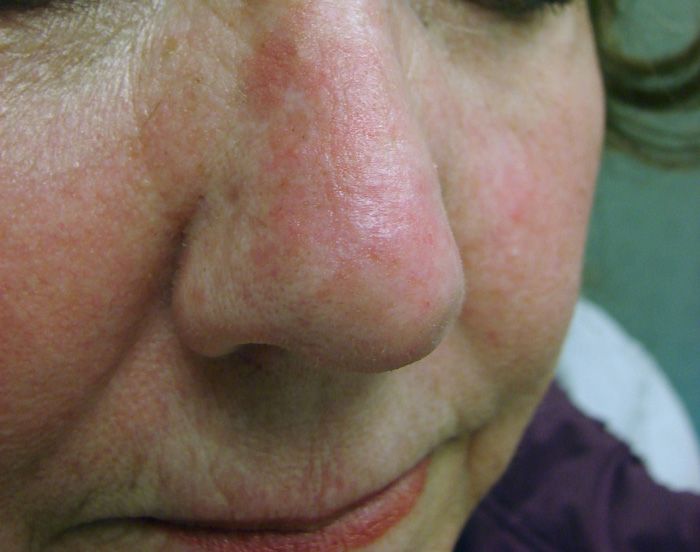
A 67-year-old woman noted a gradually increasing, asymptomatic redness of her nose.
Key points: The nose demonstrated nearly confluent erythema and roughness to touch on the anterior and right lateral surfaces. The patient has a history of actinic keratoses and basal cell carcinomas. This picture represents a fairly severe degree of photodamage with an extensive area of actinic keratosis. The latter may be referred to as proliferating actinic keratosis.
Treatment: It would be almost inhumane to treat this patient with liquid nitrogen cryosurgery. As a consequence, the affected area was treated with 3.75% imiquimod cream, daily for 2 weeks, followed by a 2 week drug holiday, and then by a second 2 week daily application. Although the area turned very red and was somewhat tender during therapy, the whole lesion was ablated.
Note: Use of a topical therapy to achieve clearance of a field of actinic damage can be done with imiquimod (5% and 3.75% creams), 5-fluorouracil (0.5%, 2% and 5% creams), ingenol mebutate (0.015% cream) or diclofenac 3% gel. Each therapy has its own advantages and disadvantages.
