- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Idiopathic Localized Hypertrichosis
A 22-year-old Chinese man presented with a patch of increased hair growth on his back. The hair first appeared 9 years earlier, and the area of growth slowly expanded until 3 years ago.
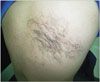
A 22-year-old Chinese man presented with a patch of increased hair growth on his back (Figure 1). The hair first appeared 9 years earlier, and the area of growth slowly expanded until 3 years ago.
The patient took no medications. He had not applied any chemical over the affected area. He had chickenpox at age 5 years, but there was no residual scarring. He reached puberty at age 12 years and married at age 20 years. There was no family history of hypertrichosis or hirsutism.
Physical findings were otherwise normal; no dysmorphic features or organomegaly was noted. The pustule in the hair-bearing area was an incidental finding.
Idiopathic localized hypertrichosis was diagnosed. The patient was reassured of the benign nature of the condition.(Discussion continues on next page.)
HYPERTRICHOSIS: AN OVERVIEW
Hypertrichosis refers to the increased growth of vellus or other hair at inappropriate locations beyond the normal variation for a patient's reference group.1 The affected areas have a greater number of hair follicles than is normal for the body site.1 The condition is unrelated to androgen excess and unaccompanied by virilism or menstrual abnormalities.2 Hypertrichosis can be generalized or localized and may be congenital or acquired.
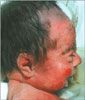
Congenital generalized hypertrichosis may result from maternal ingestion of medications (such as minoxidil, phenytoin, and diazoxide) or alcohol, or it may be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern (eg, hypertrichosis lanuginosa, universal hypertrichosis, or hypertrichosis with gingival hyperplasia) or X-linked dominant pattern.1-3 Generalized hypertrichosis is also a feature of many syndromes, notably Brachmann–de Lange syndrome (also known as Cornelia de Lange syndrome) (Figure 2), Ambras syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, Coffin-Siris syndrome, Laband syndrome, Hunter syndrome, Hurler syndrome, Sanfilippo syndrome, Bloom syndrome, Seckel syndrome, Gorlin syndrome, Cowden syndrome, Seip-Berardinelli syndrome, Donohue syndrome, Barber-Say syndrome, stiff skin syndrome, Winchester syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 3q, and Schinzel-Giedion syndrome.1,3,4

Congenital generalized hypertrichosis may also be familial, with a multifactorial mode of inheritance (Figure 3).

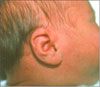
Congenital localized hypertrichosis is a notable feature of congenital melanocytic nevi (Figure 4), congenital Becker nevi, nevoid hypertrichosis, nevus pilosus, smooth muscle hamartomas, plexiform neurofibromas, and linear epidermal nevi.3,5-7 This localized type may be associated with an underlying spina bifida occulta, diastematomyelia, or kyphoscoliosis.8 Hypertrichosis of the pinnae is most commonly seen in patients with XYY syndrome and in infants of mothers who have diabetes mellitus (Figure 5).3,9,10
Hypertrichosis cubiti (hairy elbows) and anterior cervical hypertrichosis are associated with both autosomal dominant and recessive inheritance patterns, although they may be idiopathic.11,12
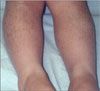
Acquired generalized hypertrichosis is most frequently caused by medications, such as phenytoin (in 5% to 10% of patients), cyclosporine, danazol, minoxidil, penicillamine, diazoxide, psoralens, anabolic agents, corticosteroids, acetazolamide, hexachlorobenzene, and streptomycin.1,3 Typically, phenytoin-induced hypertrichosis occurs to a greater extent on the extremities than on the face and trunk (Figure 6).3 In contrast, minoxidil-induced hypertrichosis characteristically involves the face, shoulders, and extremities.13
Drug-induced hypertrichosis usually resolves within months after the offending agent is discontinued. Acquired generalized hypertrichosis may also result from starvation, neoplasm, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, acrodynia, porphyria, dermatomyositis, and hypothyroidism.2,14
Acquired localized hypertrichosis arises after chronic irritation, friction, or inflammation and may develop around chickenpox scars, the sites of insect bites, at the periphery of burned skin, and on the legs after radical inguinal lymphadenectomy.1,2 The condition has also been noted after topical use of hydrocortisone, after the application of a plaster of Paris cast or fiberglass cast, after x-ray or UV irradiation, and in patients with mental illness who repeatedly bite or scratch their hands and arms.2,15-17
CLINICAL EVALUATION
Hypertrichosis must be distinguished from hirsutism, or excessive male-pattern hair growth that results from an excess of androgens.18 Hirsutism is characterized by excessive coarse hair on areas of the body that are sensitive to androgens and where there is normally very little hair, especially in females.18 These androgen-dependent areas include the upper lip, chin, cheeks, chest, lower abdomen, and inner aspects of the thighs.18 Other signs and symptoms of androgen excess (or virilism) include clitoromegaly, acne, frontal balding, increased muscularity, loss of female body contour, deepening of the voice, increased sebum output, and changes in libido.
The history should include the age at onset and the site and progression of the increased hair growth. Ask about the use of medications, onset of puberty, menstrual irregularities, concomitant illnesses, past health, family history of increased hair growth, and ethnic background.19 Document the area of increased hair growth. If it occurs in androgen-dependent areas, abnormalities of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and gonads must be ruled out-particularly in patients with signs of virilism.
No laboratory testing is necessary for patients with hypertrichosis. However, if hirsutism is suspected, serum levels of dehydroepiandrosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and testosterone and urinary 17-keto- steroids should be measured.18,19
MANAGEMENT
Treat the underlying cause whenever possible. Offending pharmacological agents should be discontinued. Patients with hypertrichosis can conceal the hair with makeup or lighten it with over-the-counter bleaching cream.1 Mechanical methods to remove unwanted hair include cutting with scissors, shaving with a razor or electrical shaver, plucking, chemical or wax epilation, electrolysis, intense light therapy, and laser hair removal.18,20
References:
REFERENCES:
1. Wendelin DS, Pope DN, Mallory SB. Hypertrichosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:161-179.
2. Leung AK, Kiefer GN. Localized acquired hyper-trichosis associated with fracture and cast application. J Natl Med Assoc. 1989;81:65-67.
3. Olsen EA. Hypertrichosis. In: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N, eds. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing, 2006:1772-1782.
4. Barisic I, Tokic V, Loane M, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of Cornelia de Lange syndrome in Europe. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A:51-59.
5. Schaffer JV, Chang MW, Kovich OI, et al. Pigmented plexiform neurofibroma: distinction from a large congenital melanocytic nevus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:862-868.
6. Leung AK. Giant congenital nevomelanocytic nevus. Can J CME. 2006;18(5):68.
7. Leung AK, Fong JH. Non-hairy Becker's nevus. Can J Diagn. 2004;21(2):47.
8. Izci Y, Gonul M, Gonul E. The diagnostic value of skin lesions in split cord malformations. J Clin Neurosci. 2007;14:860-863.
9. Akcakus M, Koklu E, Kurtoglu S, et al. Neonatal hypertrichosis in an infant of a diabetic mother with congenital hypothyroidism. J Perinatol. 2006;26:256-258.
10. Leung AK, Rafaat M. Hypertrichosis pinnae. Consultant. 2002;42:647.
11. Braddock SR, Jones KL, Bird LM, et al. Anteriorcervical hypertrichosis: a dominantly inherited isolated defect. Am J Med Genet. 1995;55:498-499.
12. Reed OM, Mellette JR, Fitzpatrick JE. Familial cervical hypertrichosis with underlying kyphoscoliosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:1069-1072.
13. Earhart RN, Ball J, Nuss DD, Aeling JL. Minoxidil-induced hypertrichosis: treatment with calcium thioglycolate depilatory. South Med J. 1977;70:442-443.
14. Wyatt JP, Anderson HF, Greer KE, Cordovo KM. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa as a presenting sign of metastatic prostate cancer with rapid resolution after treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;56:S45-S47.
15. Hengge UR, Ruzicka T, Schwartz RA, Cork MJ. Adverse effects of topical glucocorticosteroids. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:1-15.
16. Leung AK. Hypertrichosis associated with topical hydrocortisone. Hong Kong J Pediatr. 1986;1:11-13.
17. Namazi MR. UV light may induce hypertrichosis through production of PGE2. Med Hypotheses. 2007;68:917-918.
18. Leung AK, Robson WL. Hirsutism. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:773-777.
19. Leung AK, Robson WL. Premature adrenarche. J Pediatr Health Care. In press.
20. Vashi RA, Mancini AJ, Paller AS. Primary generalized and localized hypertrichosis in children. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137:877-884.
Atopic Dermatitis: The Pipeline and Clinical Approaches That Could Transform the Standard of Care
September 24th 2025Patient Care tapped the rich trove of research and expert perspectives from the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis 2025 conference to create a snapshot of the AD care of the future.
