- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Dupilumab Efficacy for Severe Atopic Dermatitis Durable at 5 Years: New Data
After 60 months of treatment, 38% of study participants with severe AD achieved complete remission.
More than one-third of patients with severe atopic dermatitis (AD), a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the skin and skin barrier defects, were in complete remission after taking dupilumab (Dupixent; Sanofi-Regeneron) for 5 years, according to a new study.
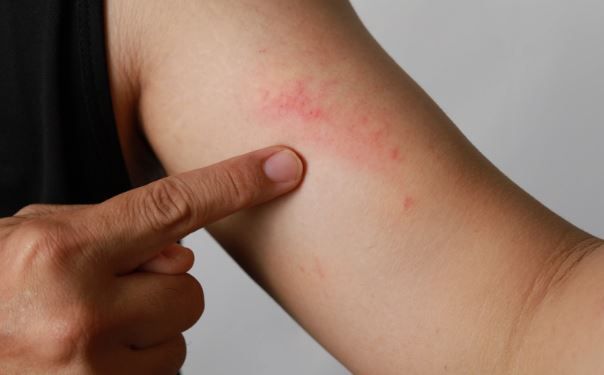
The research, published in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment, analyzed data from more than 700 patients receiving dupilumab. Led by Francesca Barei, MD, of Fondazione IRCCS Ca' Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico in Milan, Italy, is only the second to look at real world results for patients on the therapy for 5 or more years. The study found that over 60 months of treatment, 38% of patients achieved complete remission, while 91% experienced at least a 90% improvement in their eczema scores. Additionally, 83% of patients reported either no itch or only mild itching.
“This investigation establishes dupilumab’s enduring efficacy and safety in severe AD, emphasizing its potential as a sustained therapeutic option over 5+ years,” the study authors wrote.
The researchers also looked at factors that might predict why some patients stop treatment, finding people with a specific type of the condition, called nummular eczema, characterized by round, coin-shaped patches of inflamed skin had a higher risk of developing psoriasis while on dupilumab, leading them to discontinue taking the medicine. This was the first research paper to report the correlation, study authors wrote.
While the occurrence of dupilumab -associated psoriasis is a known adverse event, this finding suggests that patients with certain atopic dermatitis phenotypes may require closer monitoring during treatment.
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-4, which has a cascading effect on the production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Other systematic therapies for AD include lebrikizumab (Ebglyss), abrocitinib (Cibinqo) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq).
Source: Barei F, Calzari P, Valetellini L, et al. Five-year real-world drug survival of dupilumab in severe atopic dermatitis and associate predictors. J Dermatologic Treat. Published October 13, 2024. doi:10.1080/09546634.2024.2404718
Atopic Dermatitis: The Pipeline and Clinical Approaches That Could Transform the Standard of Care
September 24th 2025Patient Care tapped the rich trove of research and expert perspectives from the Revolutionizing Atopic Dermatitis 2025 conference to create a snapshot of the AD care of the future.
