- Clinical Technology
- Adult Immunization
- Hepatology
- Pediatric Immunization
- Screening
- Psychiatry
- Allergy
- Women's Health
- Cardiology
- Pediatrics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- Pain Management
- Gastroenterology
- Infectious Disease
- Obesity Medicine
- Rheumatology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Pulmonology
Agitation and Auditory Hallucinations: Is it the HCTZ?
A 65-year-old woman presents to the ED oriented only x2 and hearing her dead mother's voice. HCTZ is her only Rx. What's your diagnosis?
Figure 1. Examples of mydriasis; not actual patient
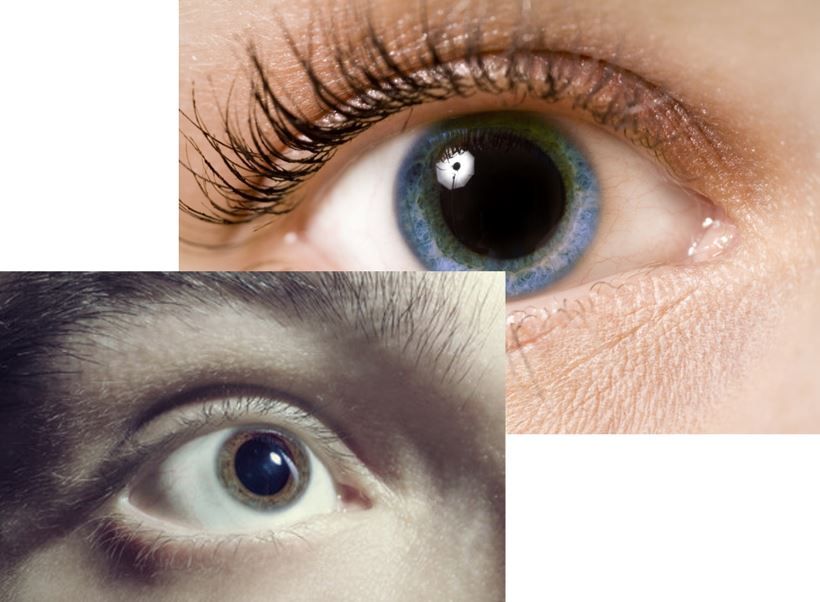
Figure 2.

History of Present Illness
A 65-year-old woman who was supposedly taking only HCTZ for hypertension is brought to the emergency department by family for agitation and confusion that has been getting progressively worse for the past month, especially today. There has been no trauma, pain, dyspnea, fever, loss of appetite, or other symptoms. The patient denies any complaints but is oriented only x2 and says she keeps hearing her dead mother’s voice.
Vital Signs & Physical Exam
Vital signs are normal except for a pulse of 119 beats/min and a temperature of 99.5°F. Physical exam is normal except for confusion, auditory hallucination, and dilated pupils, bilaterally, even in bright light (see Figure 1 for examples only; not actual patient).
What would you inlcude in your initial differential diagnosis?
What initial tests would you order?
ANSWERS
What would you inlcude in your initial differential diagnosis?
- Brain lesion
- Infection
- Medication or drug toxicity
- Syphilis, the great imitator
What initial tests would you order?
- CBC and BMP: results of both were normal
- Brain MRI: also found to be normal
What are the primary causes of mydriasis (enlarged pupils)?
What should you do next?
Next: Answers, discussion, and case conclusion
ANSWERS
- What are the causes of mydriasis? See highlighted area in Figure at right.
- What should you do next? Hold all medications and admit for observation.
Discussion
Mydriasis has multiple potential causes. Unilateral mydriasis can be physiologic (Adie tonic pupil; aka, Holmes-Adie Syndrome) or can be caused by trauma, damage to cranial nerve 3, topical medications, or plant sap that gets into only one eye. When the mydriasis is unchanged after instilling pilocarpine drops, it is likely the result of something that got into the eye.
Bilateral mydriasis is usually caused by drug or medication toxicity although a few uncommon diseases such botulism and diphtheria can also be causative. The bilateral presentation can also be caused by an agent that gets into both eyes. A useful mnemonic for bilateral mydriasis is “BALD CATS,” highlighted in the Figure above. (Sample page courtesy of The Emergency Medicine 1-Minute Consult Pocketbook; please click on Figure to enlarge).
Case Conclusion
Toxicology screen was negative for presence of amphetamines and cocaine, but was positive for metabolites of marijuana and opiates. No infection was found; the patient did improve after a few days in the hospital off all medication. It was thought that the toxicity was most likely related to an anticholinergic agent. Once the patient was back to baseline she admitted to taking a lot of Benadryl because both the marijuana and the Norco she got from her “friend” made her itchy. This would explain confusion, dilated pupils, tachycardia, and low grade fever.
